GS508 – ALM for Compliance Features in Globalization Studio
When you’re managing tax rules, electronic invoices, or document formats in multiple environments (like Dev, UAT, and Production), you need a smart way to move your configurations from one place to another without errors or rework.
This is where ALM (Application Lifecycle Management) comes in.
In this article, you’ll learn:
- What ALM means for Globalization Studio
- How to use Dataverse and Power Platform solutions to manage features
- A simple step-by-step guide to move your configurations safely across environments
If you’re new to repositories and features, read GS503 – Getting Started with the Workspace and GS505 – Creating a Feature from Scratch first.
Table of Contents
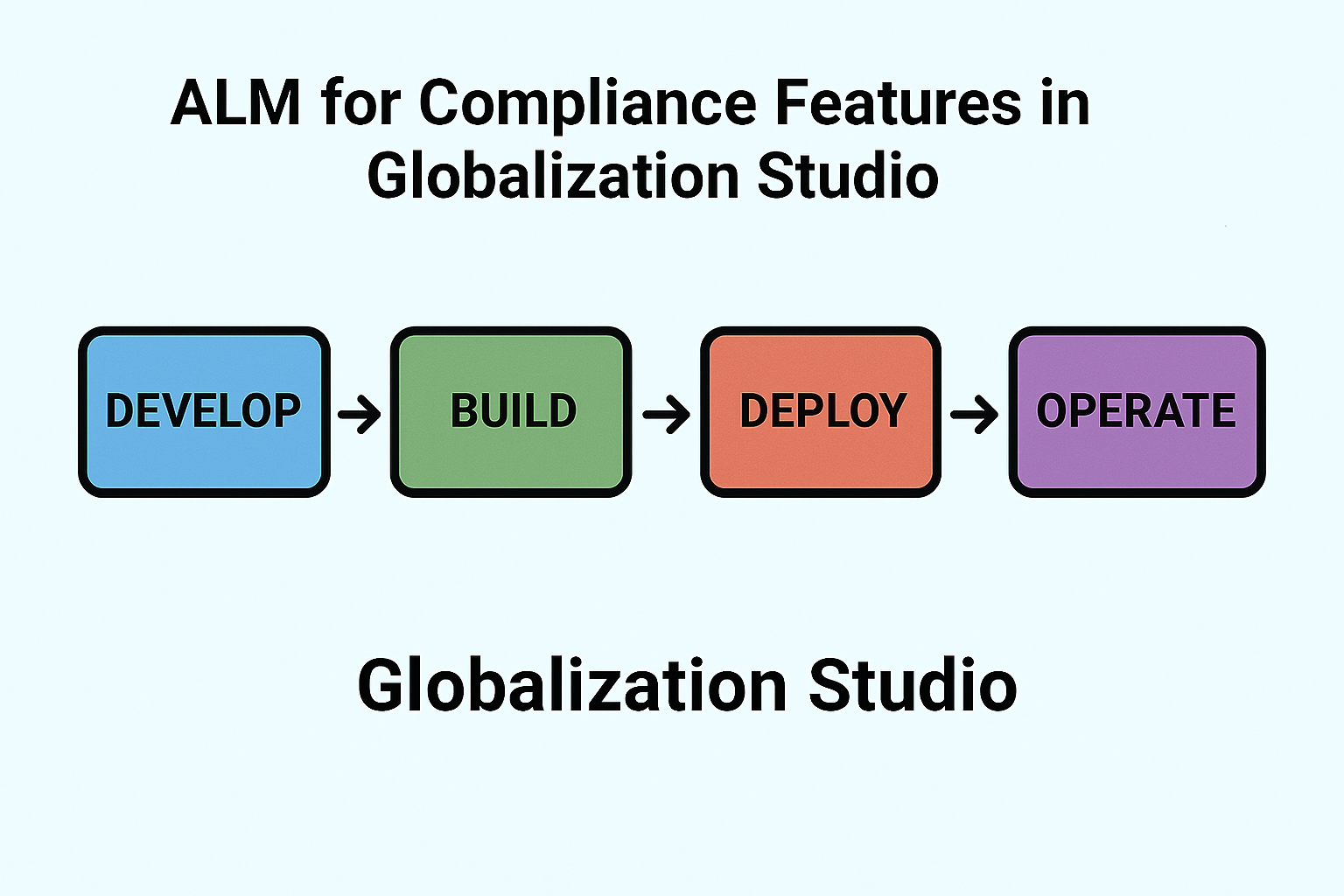
Toggle🧠 What Is ALM in Globalization Studio?

ALM is the process of managing the life of a configuration or feature, from development to testing to production, without rebuilding it manually each time.
In Globalization Studio, ALM is possible because:
- All features are stored in Dataverse
- These solutions can be exported and imported into other environments (just like apps in Power Platform)
💡 Think of it like a suitcase: a solution is a bag where you pack all your features and take them from Dev to UAT to Prod.
📦 What Is a Solution?
A solution is a container in Dataverse that holds:
- Your globalization features (tax, invoicing, etc.)
- Related ER configurations
- Version history and status
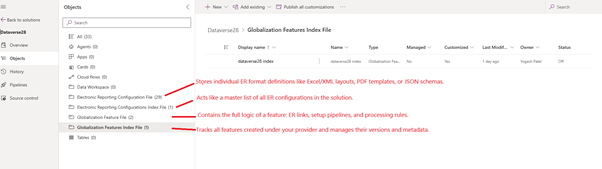
Solutions are the easiest way to:
- Package your work
- Export it as a .zip
- Share it with other environments or teams
🛠️ How to Use ALM – Step-by-Step
Let’s say you’ve finished building a new Spain e-invoicing feature in your Dev environment. Now, you want to move it to UAT.
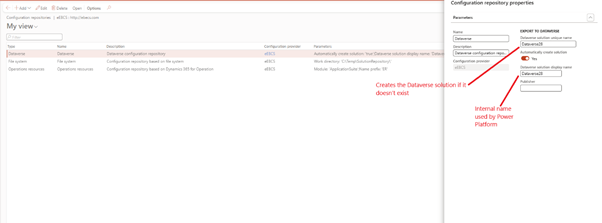
✅ Step 1: Configure Dataverse Repository property in Dev (Note – Environment must be higher than Tier-1)
- Go to the Globalization Studio workspace
- Select configuration provider > Dataverse > Configuration Repository properties
- Setup parameters and give meaningful name to solution Name
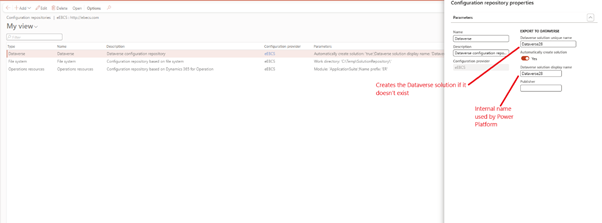
- Click OK
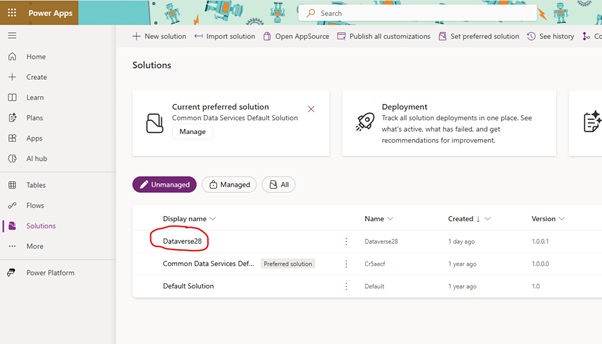
- This creates solution in Power app platform with same name
- All the features you create or modify will now be saved under this solution.
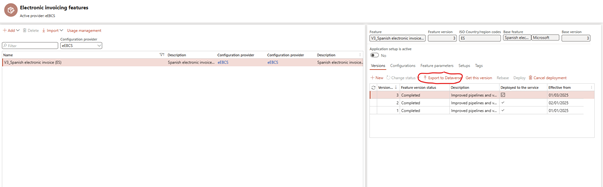
✅ Step 2: Export Features to the dataverse
- Export your completed features to dataverse
✅ Step 3: Setup Power Platform Pipeline
- Follow Microsoft documentation – https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/power-platform/alm/custom-host-pipelines
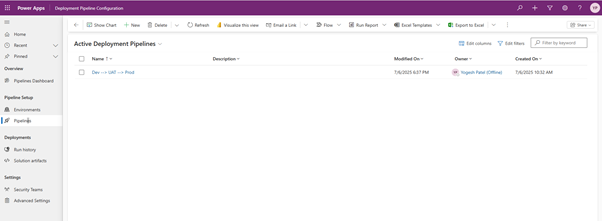
🧪 Tip: Use a managed solution for production, and an unmanaged solution for development.
✅ Step 4: Run Pipeline from Source environment
- Go to Solutions
- Click Pipeline
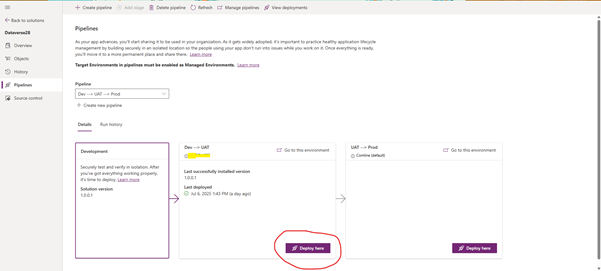
- Click Deploy button

- Check history for any error logged
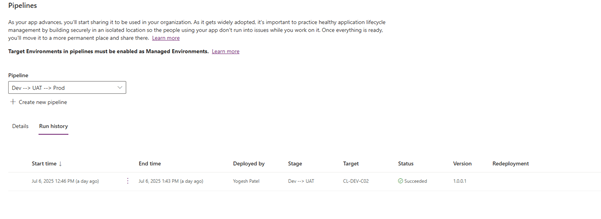
- Solution is deployed in Target environment

- Import/update feature or changes from dataverse repository in target environment
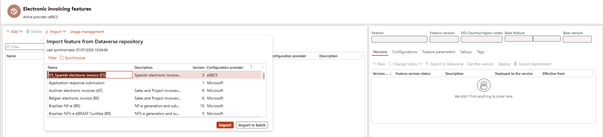
Now, your features, ER formats, pipelines, and rules are available in that environment!
📌 Note: You still need to deploy the features manually inside the Globalization Studio workspace of that environment.
🔁 What If You Just Export a Feature?
You can also export/import individual features from the feature version page, but this doesn’t handle dependencies (like shared ER configs or tags). That’s why using a solution is the better approach for full ALM.
🔐 Who Can Do This?
To use ALM across environments:
- You must have Dataverse admin access
- Your D365FO environment must be linked to Power Platform
- You should have Dataverse repository enabled in Feature Management
✅ These are covered in GS502 – From RCS to Globalization Studio
📋 ALM Checklist
| Task | Completed? |
| Created a solution in Dev | ✅ |
| Assigned features to solution | ✅ |
| Exported solution | ✅ |
| Imported solution to UAT/Prod | ✅ |
| Deployed features in target | ✅ |
💡 Why ALM Is So Helpful
| Benefit | What It Means for You |
| ✅ Save time | No need to rebuild features manually |
| ✅ Reduce errors | Everything is version-controlled and consistent |
| ✅ Stay compliant | All environments use the same logic |
| ✅ Easy rollback | Restore a previous solution version if needed |
🧭 Related Articles
- GS503 – Connecting to the Repository
- GS505 – Creating Your Own Features
- GS510 – Reusing and Adapting ER Features
- GS513 – Business Document Management with ALM
📘 Coming Up Next
In GS509 – Electronic Reporting Basics, we’ll step away from features for a moment and explain how ER (Electronic Reporting) fits into everything:
- How to build and use ER models and formats
- How to link them to Globalization Features
- Real examples for XML, Excel, and JSON
📖 [Continue reading: GS509 – Electronic Reporting Basics →]
I am Yogeshkumar Patel, a Microsoft Certified Solution Architect and Enterprise Systems Manager with deep expertise across Dynamics 365 Finance & Supply Chain, Power Platform, Azure, and AI engineering. With over six years of experience, I have led enterprise-scale ERP implementations, AI-driven and agent-enabled automation initiatives, and secure cloud transformations that optimise business operations and decision-making. Holding a Master’s degree from the University of Bedfordshire, I specialise in integrating AI and agentic systems into core business processes streamlining supply chains, automating complex workflows, and enhancing insight-driven decisions through Power BI, orchestration frameworks, and governed AI architectures. Passionate about practical innovation and knowledge sharing, I created AIpowered365 to help businesses and professionals move beyond experimentation and adopt real-world, enterprise-ready AI and agent-driven solutions as part of their digital transformation journey. 📩 Let’s Connect: LinkedIn | Email 🚀
















Post Comment