
PM503 – Setting Up the Basics for Project Management and Accounting in D365 Finance
Table of Contents
ToggleIntroduction
To unlock the full potential of Project Management in Dynamics 365 Finance, it’s crucial to get the setup right. A solid foundation ensures your projects run smoothly, with accurate tracking of costs, resources, and revenue. In this guide, we’ll walk you through the essential prerequisites and provide real-life examples to illustrate their importance.
Why Proper Setup Matters
Think of project setup as laying the groundwork for a building. Without it, you’re left with a shaky structure prone to inefficiencies and errors. By configuring key settings and parameters, you enable:
- Accurate Costing and Budgeting: Ensure every dollar is accounted for.
- Seamless Reporting: Get insights into project progress and profitability.
- Efficient Resource Management: Assign resources correctly and track utilization.
- Intercompany Collaboration: Streamline operations across multiple legal entities.
Basic Setup
Before diving into project creation, make sure these critical configurations are in place:
Project Calendar
- Purpose: Defines working days, hours, and holidays.
- Setup Steps:
- Navigate to Organization Administration > Setup > Calendars
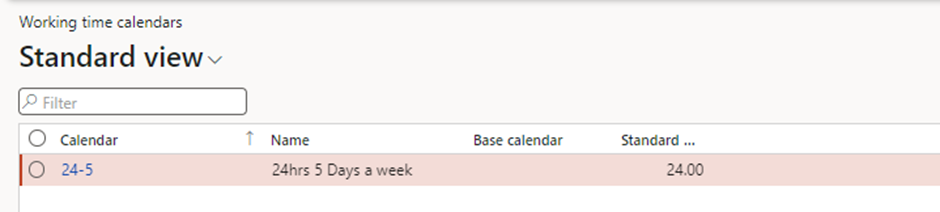
- Create a calendar and specify working times.
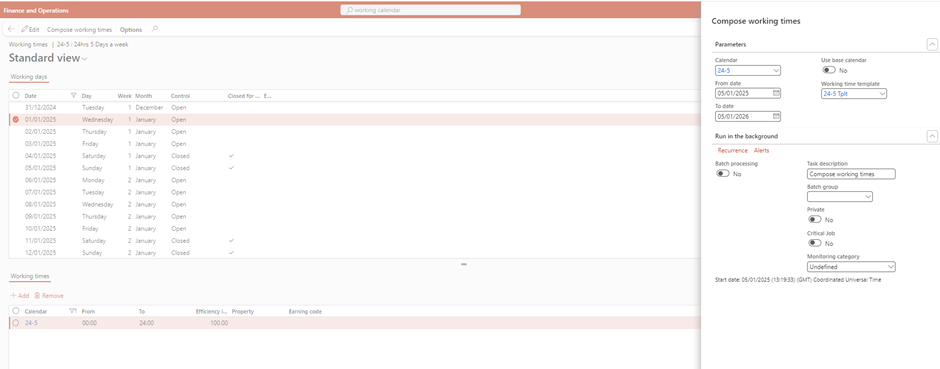
- Link the calendar to your project parameters.
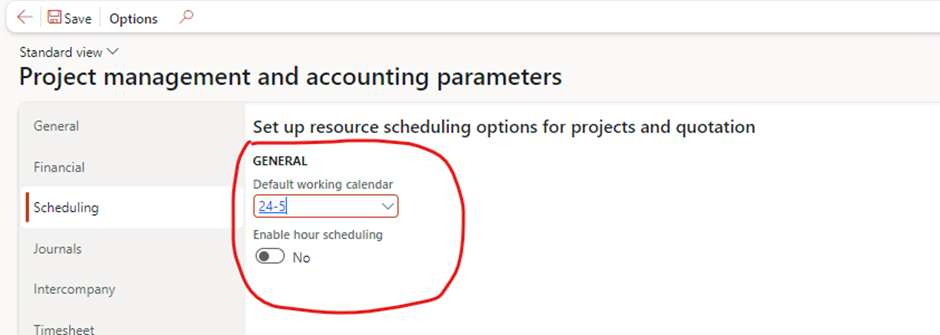
Category Groups
- Purpose: Organizes project categories for reporting, analyzing project transactions, and ensuring accurate posting to the general ledger.
- Setup Steps:
- Go to Project management and accounting > Setup > Categories > Category groups.
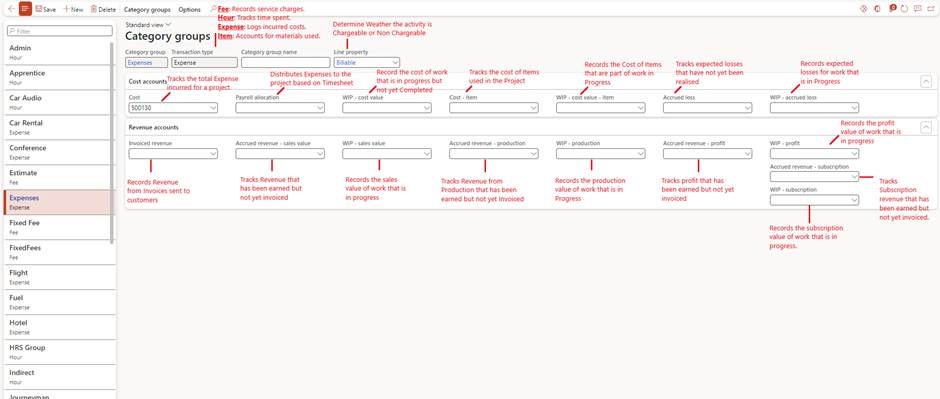
Line Properties
- Purpose: Line properties define specific characteristics of project transactions, such as whether they are chargeable to a customer, if costs should be capitalized, or if additional cost or sales percentages should be applied. They help in managing how transactions are processed and reported
- Setup Steps:
- Go to Project management and accounting > Setup > Line Properties > Line Properties.
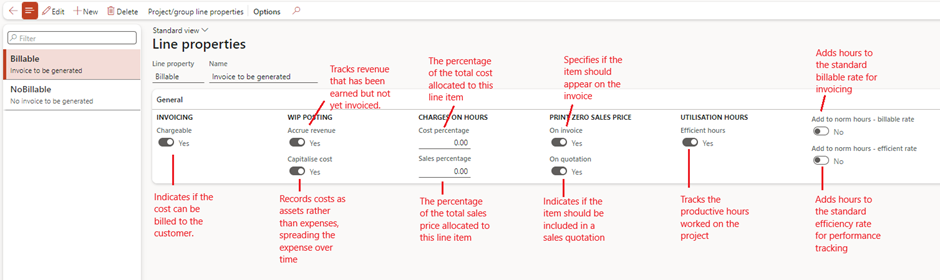
Shared Categories
- Purpose: Ensures consistency across legal entities.
- Setup Steps:
- Set up shared categories under Go to Project management and accounting > Setup > Categories > Shared Categories.
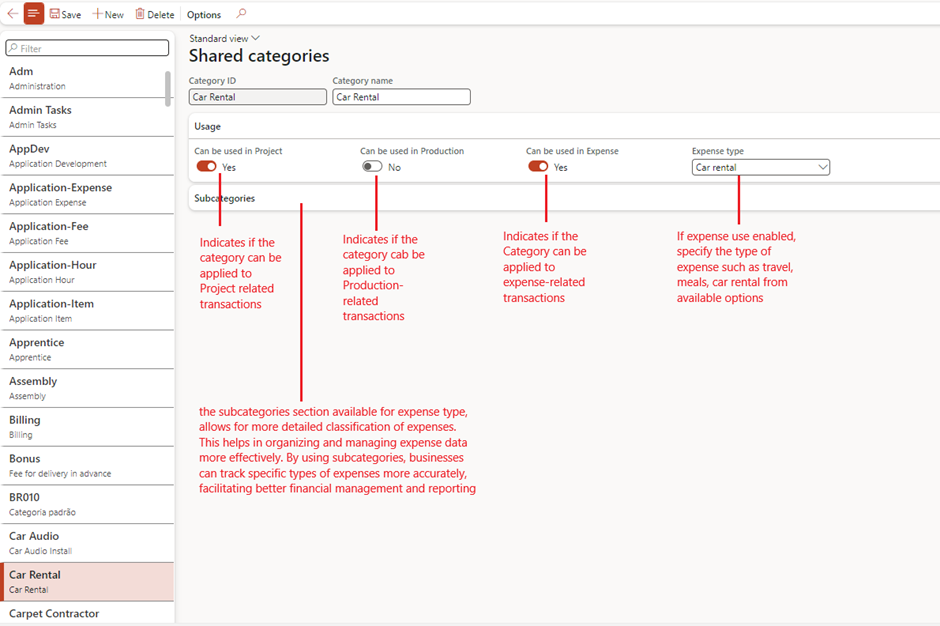
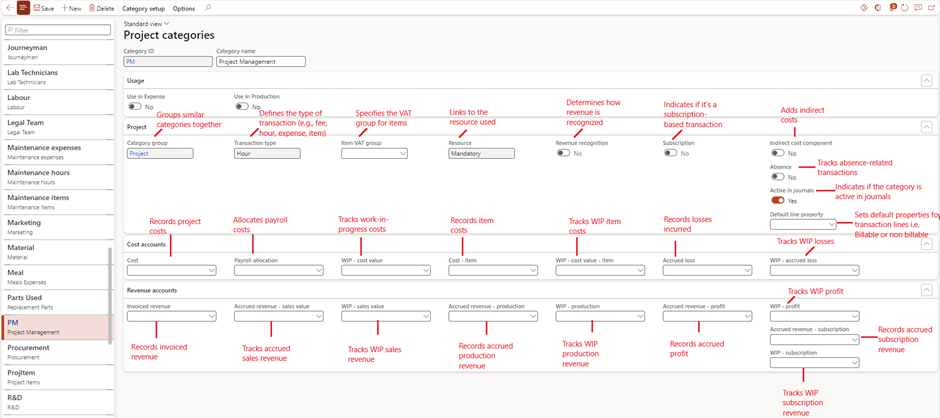
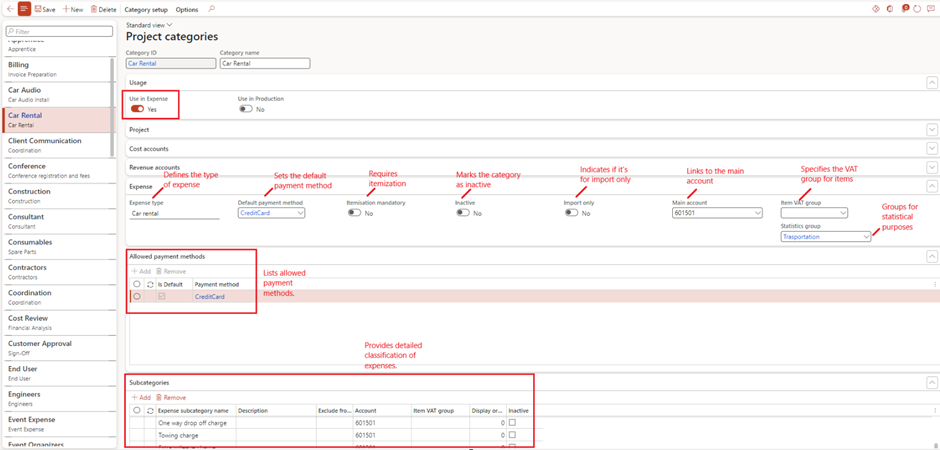
Project Categories
- Purpose: Defines specific expense and revenue types.
- Setup Steps:
- Navigate to Project management and accounting > Setup > Categories > Project categories.
- Assign shared categories and define usage (e.g., hours, items, expenses).
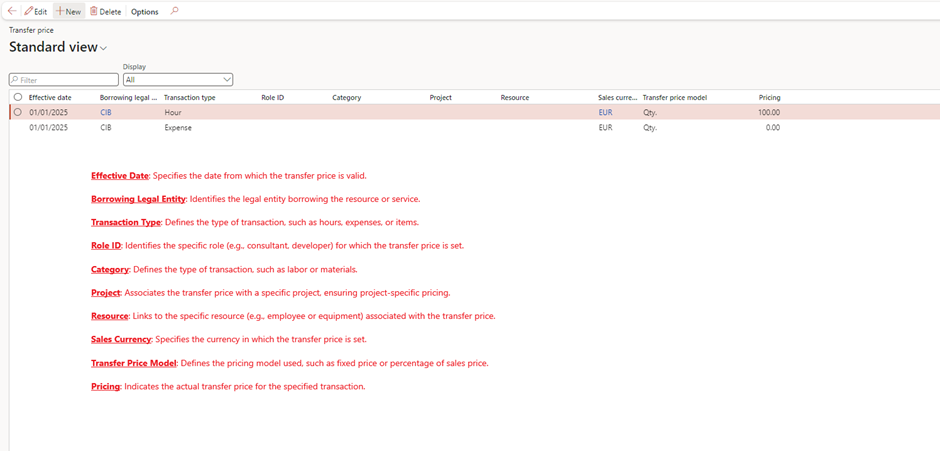
Cost Price and Sales Price (Optional)
- Purpose: Sets default pricing for labor, materials, and other project costs.
- Setup Steps:
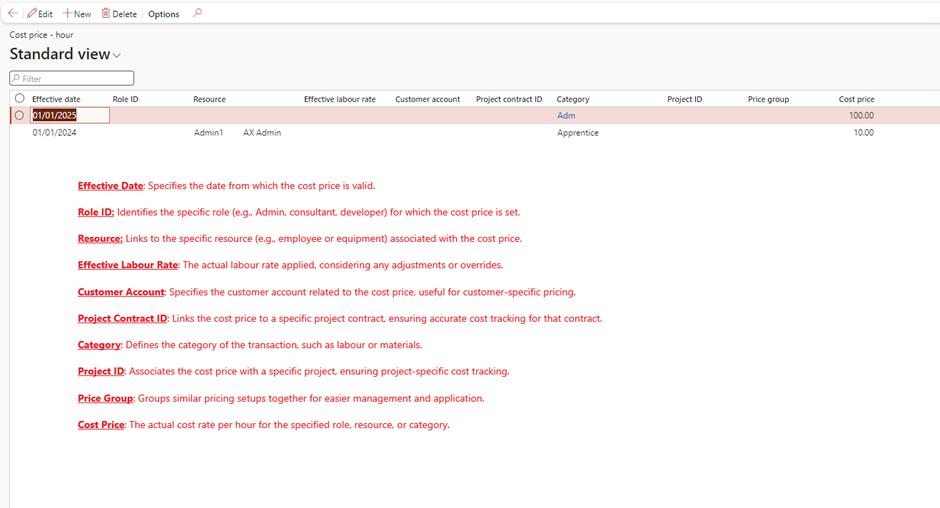
- Define cost prices under Project management and accounting > Setup > Prices > Cost price (hours)
- Purpose: Defines the internal cost of one hour of work performed by a resource.
- Example: If a consultant’s internal cost is £50/hour, this is the rate used to calculate project costs.
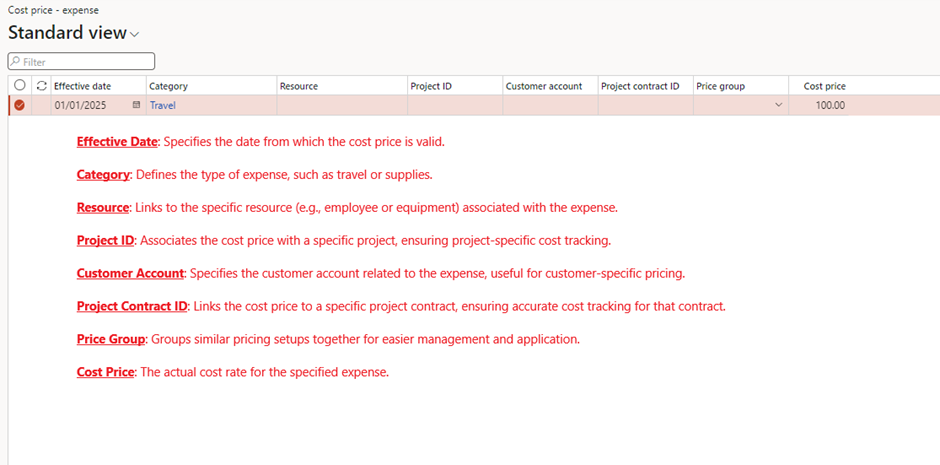
2. Set sales prices for billing under Project management and accounting > Setup > Prices > Cost Price (expense).
- Purpose: Defines the internal cost for project-related expenses like travel or accommodation.
- Example: If a hotel stay costs £200, this is recorded as the expense cost in the project.
3. Set sales prices for billing under Project management and accounting > Setup > Prices > Sales Price (hour).
- Purpose: Sets the price charged to the customer for one hour of work performed.
- Example: If the consultant’s billing rate is £100/hour, this is the sales price charged to the client.
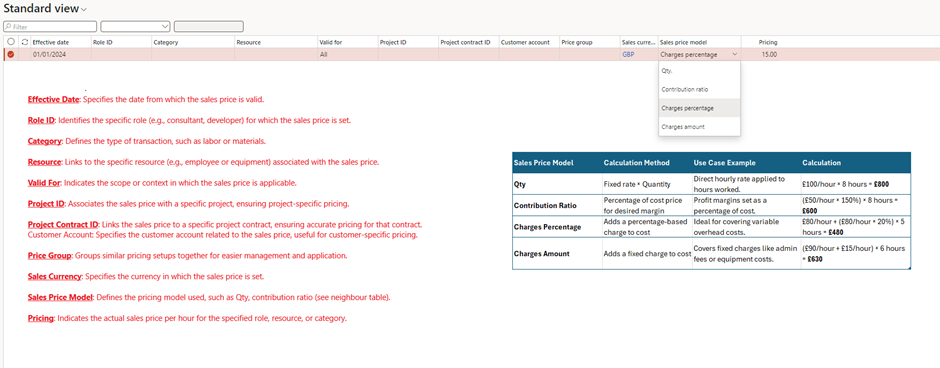
4. Set sales prices for billing under Project management and accounting > Setup > Prices > Sales Price (expense).
- Purpose: Sets the price charged to the customer for reimbursable project expenses.
- Example: If the internal hotel cost is £200, but the customer is charged £250, the sales price is £250.
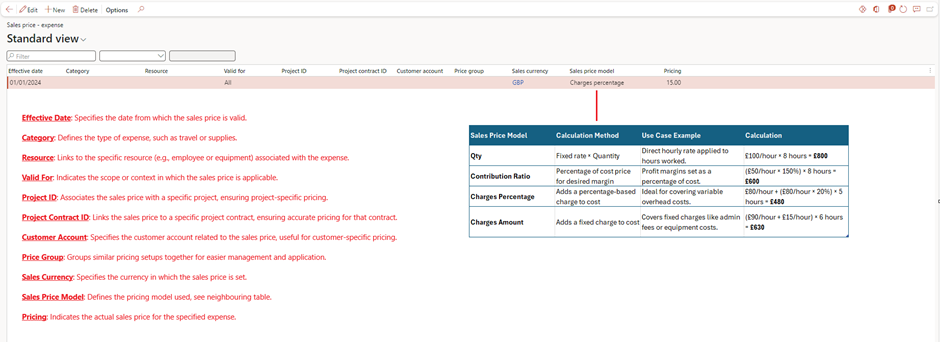
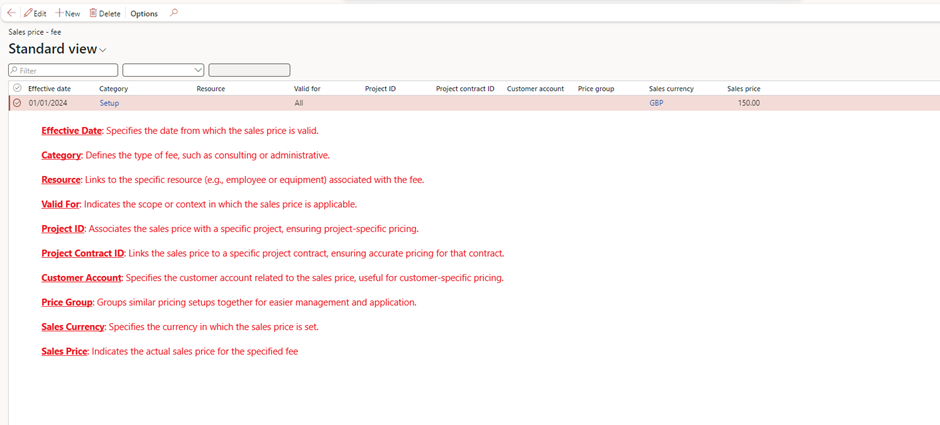
5. Set sales prices for billing under Project management and accounting > Setup > Prices > Sales Price (Fee).
- Purpose: Defines a flat fee charged to the customer for specific services or deliverables.
- Example: Charging a customer £1,000 for a project management service as a one-time fee.
6. Set sales prices for billing under Project management and accounting > Setup > Prices > Sales Price (Subscription).
- Purpose: Sets the price for recurring services or subscriptions provided to the customer.
- Example: Charging £500/month for ongoing software support.
7. Set sales prices for billing under Project management and accounting > Setup > Prices > Transfer Fee.
- Purpose: Applies an additional fee when transferring costs between internal departments or entities.
- Example: If a department transfers project work to another, a 10% transfer fee may be added to the cost price for internal accountability.
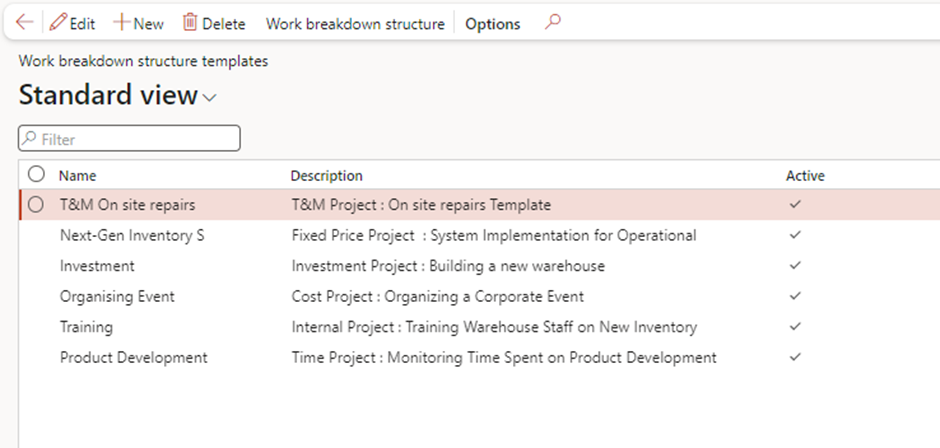
Work Breakdown Structure (WBS) Templates
Purpose
- Time Management: To outline the timeline for project tasks, ensuring they are completed on schedule.
- Resource Allocation: To determine the resources needed for each task and allocate them efficiently.
- Budget Control: To provide an overview of estimated costs for each phase or task in the project.
- Performance Tracking: To monitor project progress and ensure adherence to timelines and budgets.
Use
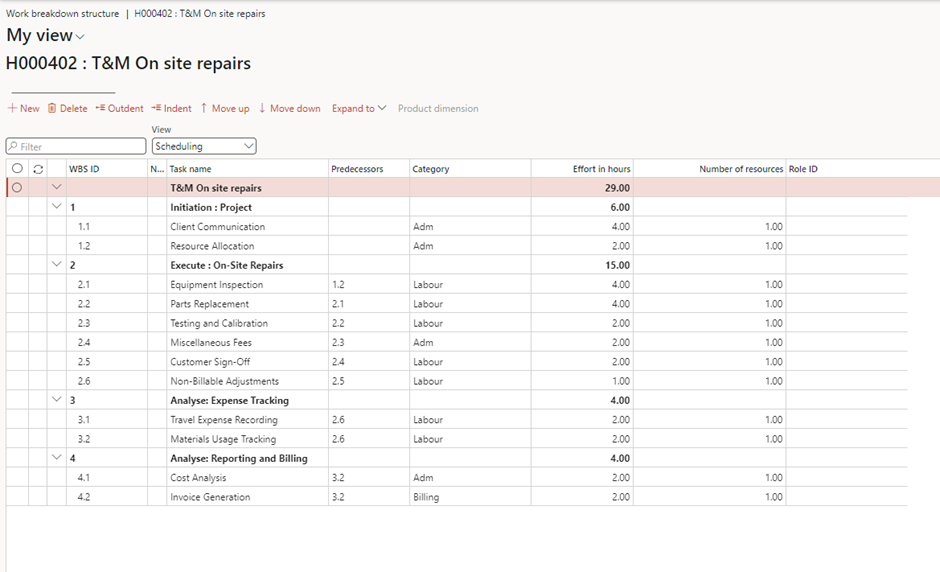
- Project Scheduling:
- Break down the project into tasks and assign start and end dates.
- Create a Gantt chart or other visual timeline to track progress.
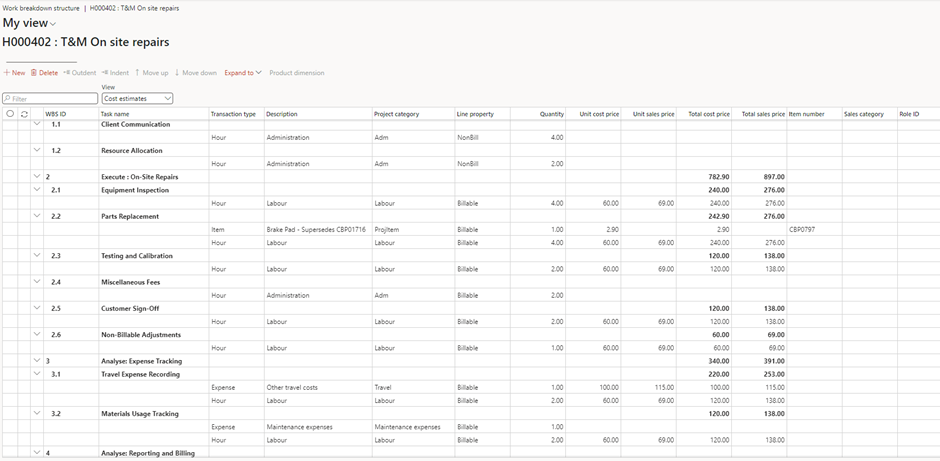
- Cost Estimation:
- Estimate costs for labor, materials, equipment, and other resources for each task.
- Aggregate task costs to determine the total project budget.
- Risk Management:
- Identify potential delays or cost overruns by comparing planned vs. actual data.
- Make adjustments to mitigate risks and keep the project on track.
- Communication:
- Share the schedule and cost estimates with stakeholders to align expectations and secure approvals.
- Setup Steps:
- Go to Project management and accounting > Setup > Projects> Work breakdown structure templates.
- Create templates for common projects
Scheduling:
Cost Estimate
Journal Setup
- Purpose: Enables recording of project transactions.
- Setup Steps:
- Set up journals for different transaction types under General ledger > Journal names.
- Types include:
- Item Journal: Tracks materials used.
- Hours Journal: Records employee time.
- Expense Journal: Logs travel, meals, and other costs.
- Fee Journal: Captures fixed fees or charges.
Ledger Posting Profile
Cost Account
Project management and Accounting > Setup > Posting > Ledger posting setup > Tab: Cost account
- Purpose: This account is used to record the costs incurred for project-related activities. It ensures that project expenses, such as labor, materials, and overhead, are correctly posted in the general ledger.
- Example:
- A consultant works 8 hours on a project at a cost price of £50/hour.
- The total cost of £400 (8 × £50) is posted to the Cost Account, such as “Consulting Expenses (Account: 5001).”
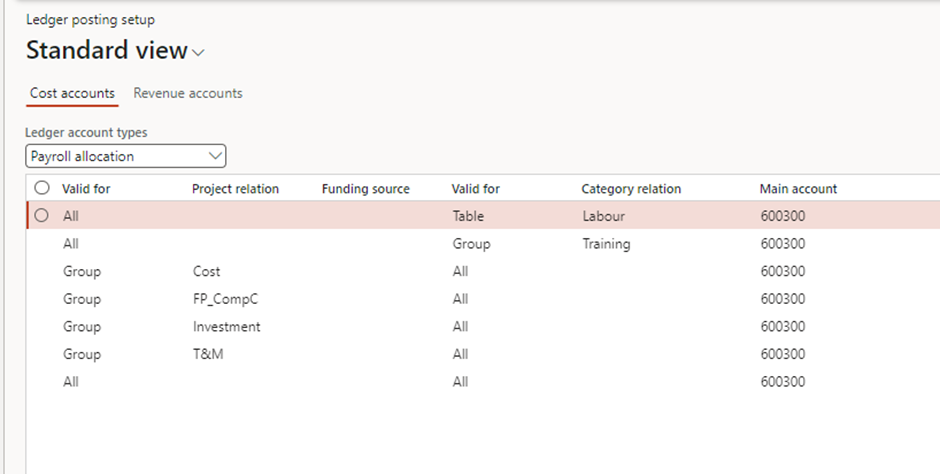
Revenue Account
Project management and Accounting > Setup > Posting > Ledger posting setup > Tab: Revenue account
- Purpose: This account is used to record the revenue generated from project-related activities, such as billing for services, expenses, or fees. It ensures that project income is accurately reflected in the general ledger.
- Example:
- A customer is billed £800 for 8 hours of consulting work at a sales price of £100/hour.
- The total revenue of £800 is posted to the Revenue Account, such as “Consulting Revenue (Account: 4001).”
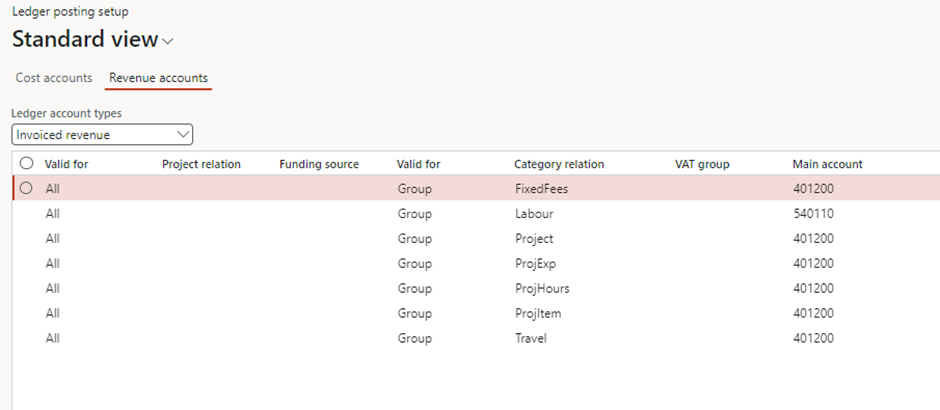
Tips for a Smooth Setup
- Test Configurations: Use a test environment to verify settings before going live.
- Standardize Processes: Create templates and guidelines for consistency across projects.
- Involve Stakeholders: Collaborate with finance, HR, and operations teams to ensure alignment.
Conclusion
Setting up the basics for Project Management and Accounting in D365 Finance might seem detailed, but it’s a one-time effort that pays dividends in efficiency and accuracy. By following these steps, you’ll be ready to tackle any project with confidence, whether it’s managing employee hours, upgrading facilities, or collaborating across entities.
Ready to get started? Dive into the setup and watch your projects run like clockwork!
Expand Your Knowledge: See More Project Management Blogs
I am Yogeshkumar Patel, a Microsoft Certified Solution Architect and Enterprise Systems Manager with deep expertise across Dynamics 365 Finance & Supply Chain, Power Platform, Azure, and AI engineering. With over six years of experience, I have led enterprise-scale ERP implementations, AI-driven and agent-enabled automation initiatives, and secure cloud transformations that optimise business operations and decision-making. Holding a Master’s degree from the University of Bedfordshire, I specialise in integrating AI and agentic systems into core business processes streamlining supply chains, automating complex workflows, and enhancing insight-driven decisions through Power BI, orchestration frameworks, and governed AI architectures. Passionate about practical innovation and knowledge sharing, I created AIpowered365 to help businesses and professionals move beyond experimentation and adopt real-world, enterprise-ready AI and agent-driven solutions as part of their digital transformation journey. 📩 Let’s Connect: LinkedIn | Email 🚀
















Post Comment