
SB505 – Subscription Billing Architecture in D365 Finance
Table of Contents
Toggle🌐 Introduction
Welcome back to the Subscription Billing Series! If you’re just joining us, we’ve already covered the basics of Subscription Billing and real-life use cases in SB501–SB504. Now, it’s time to zoom out and understand how the entire architecture is designed within Microsoft Dynamics 365 Finance.
Before we dive into configurations or industry scenarios, you must understand how the three core modules work individually—and more importantly—how they interact when used together.
In this article, we’ll break down the building blocks of Subscription Billing, the modular architecture, feature dependencies, and how each module aligns with financial reporting requirements like IFRS 15 and ASC 606.
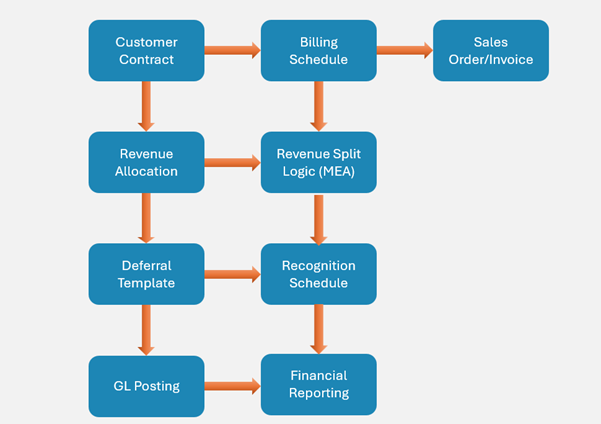
🧱 What Is Subscription Billing?
Subscription Billing in D365 Finance is a purpose-built solution to manage recurring billing, contract revenue recognition, deferrals, and compliance with complex accounting standards—all within the ERP.
Rather than relying on spreadsheets or third-party billing tools, this module brings full billing lifecycle management into your finance core. It supports:
- Recurring billing cycles
- Revenue and expense deferrals
- Bundled product revenue allocation (MEA)
🧩 Three Core Modules (Think LEGO Blocks!)
The Subscription Billing solution is made up of three independent yet interoperable modules. Each one is enabled separately via Feature Management, and you can choose to use only what you need:
Recurring Contract Billing
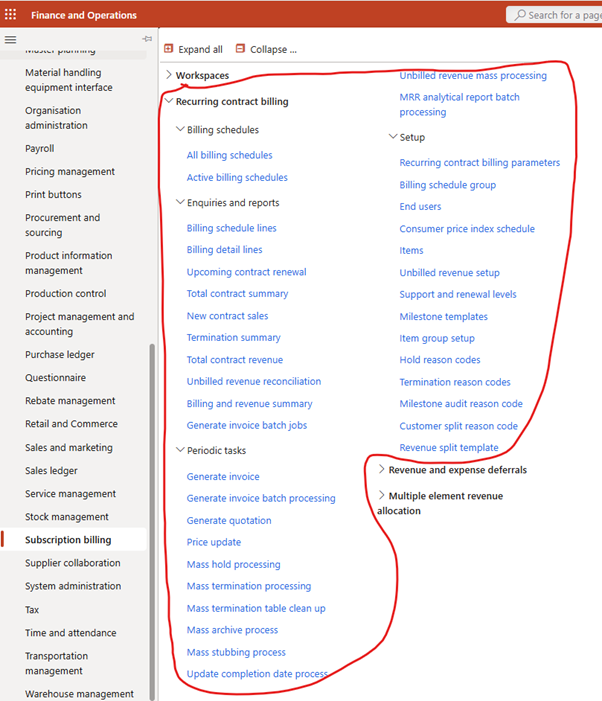
- Purpose: Automates periodic billing (monthly, annually, etc.)
- Use Cases: SaaS, leasing, telecom plans, service retainers
- Key Features:
- Billing schedules and templates
- Usage-based billing
- CPI escalations & proration
- Renewal automation
- Invoicing (Sales order or Free text)
💡 This is the “engine” that runs subscriptions. All billing schedules start here.
Revenue and Expense Deferrals

- Purpose: Automates deferral of income and expenses across periods
- Use Cases: Annual contracts paid upfront but recognized monthly
- Key Features:
- Straight-line or event-based deferrals
- Deferral templates & automation
- Integration with unbilled revenue
- GL journal automation
- Short-term vs long-term tracking
💡 This keeps your revenue recognition compliant with IFRS 15 / ASC 606.
Multiple Element Revenue Allocation (MEA)
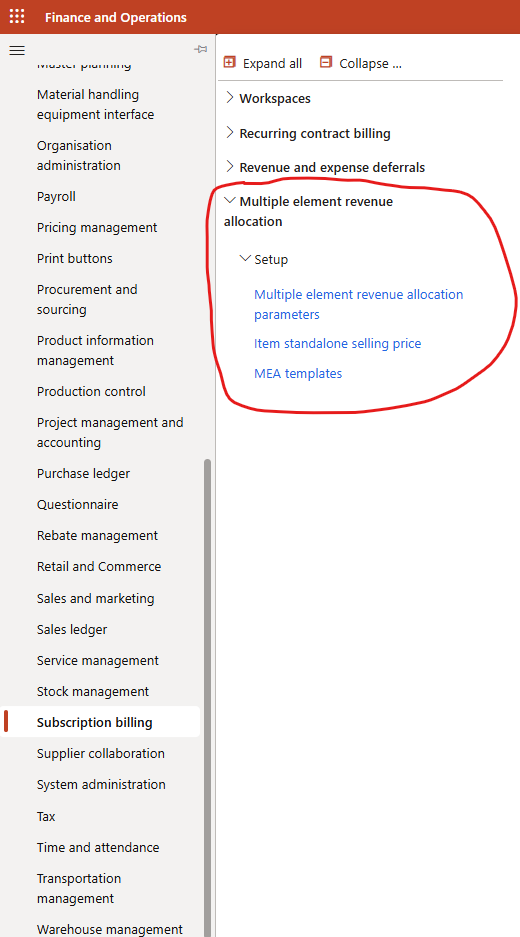
- Purpose: Handles allocation of revenue across bundled products or services
- Use Cases: “Phone + Data Plan” deals, hardware + installation bundles
- Key Features:
- Standalone selling price (SSP) logic
- Revenue split methods (percent, amount, residual)
- Parent-child item handling
- Deferred contract revenue accounting
💡 This module ensures revenue is recognized correctly, even if your invoice doesn’t match the accounting reality.
⚙️ Enabling the Modules (Important!)
Subscription Billing is disabled by default. Here’s how to enable it:
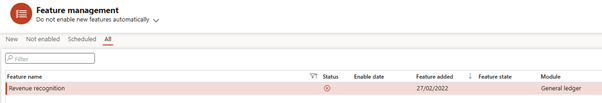
Turn off Revenue Recognition
- Go to Feature Management
- Search for “Revenue recognition”
- Disable it (since it’s not compatible with Subscription Billing)
Enable Subscription Billing
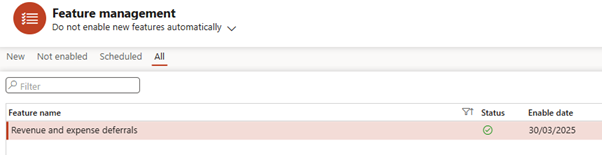
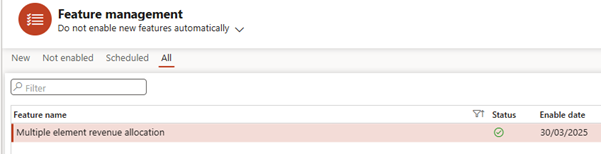
- In Feature Management, search for “Subscription billing”
- Enable the main feature, then enable the sub-features:
- Recurring Contract Billing

- Revenue and Expense Deferrals
- Multiple Element Revenue Allocation
🔁 How They Work Together (Real Example)
Let’s say your company sells a 12-month SaaS subscription with onboarding services and optional add-ons:
| Component | Billing Method | Recognition Method | Module Used |
| SaaS License | Monthly | Recognize monthly | Recurring Contract Billing + Deferral |
| Onboarding Fee | One-time | Recognize over 3 months | Recurring Contract Billing + Deferral |
| Support Plan | Monthly | Recognize monthly | Recurring Contract Billing only |
| Bundle Pricing (10% discount) | Combined | Allocated by SSP | MEA + Recurring Contract Billing |
In this example, all three modules come into play.
🔍 Why Is This Architecture Important?
✅ Flexibility
Choose only what you need. Not every business needs MEA or deferrals.
✅ Compliance
All modules support IFRS 15, ASC 606, and IFRS 16 use cases.
✅ Scalability
The solution is scalable for both SMBs and large enterprises with complex intercompany billing.
✅ Audit Readiness
Audit trails for pricing changes, deferral schedules, unbilled journals, and revenue splits.
🎓 Key Takeaways
- Subscription Billing is a modular solution designed for recurring revenue, recognition, and allocations.
- The three modules—Recurring Billing, Deferrals, MEA—can be used independently or together.
- You must disable legacy Revenue Recognition before using Subscription Billing.
- This architecture supports everything from simple monthly SaaS contracts to multi-element bundled telecom plans.
Expand Your Knowledge: See More Subscription Billing Blogs
I am Yogeshkumar Patel, a Microsoft Certified Solution Architect and Enterprise Systems Manager with deep expertise across Dynamics 365 Finance & Supply Chain, Power Platform, Azure, and AI engineering. With over six years of experience, I have led enterprise-scale ERP implementations, AI-driven and agent-enabled automation initiatives, and secure cloud transformations that optimise business operations and decision-making. Holding a Master’s degree from the University of Bedfordshire, I specialise in integrating AI and agentic systems into core business processes streamlining supply chains, automating complex workflows, and enhancing insight-driven decisions through Power BI, orchestration frameworks, and governed AI architectures. Passionate about practical innovation and knowledge sharing, I created AIpowered365 to help businesses and professionals move beyond experimentation and adopt real-world, enterprise-ready AI and agent-driven solutions as part of their digital transformation journey. 📩 Let’s Connect: LinkedIn | Email 🚀
















Post Comment