
SB514 – Configuring Revenue and Expense Deferrals in D365: All Setup Options Explained
Table of Contents
Toggle🌐 Introduction
Welcome to SB514 in our Revenue Deferrals series for Subscription Billing in Dynamics 365 Finance.
In SB513, we introduced the core concepts behind revenue deferral and why it matters for IFRS 15 and ASC 606 compliance. Now, before we jump into posting and recognition (coming in SB515), it’s time to configure the engine that makes all this work.
This article explores all setup components available in the Revenue and Expense Deferrals module. We’ll explain:
- What each setting controls
- When and why to use it
- How it supports your subscription billing lifecycle
Let’s dive into the setup options in the order they appear in D365.
⚙️ 1. Revenue and Expense Deferral Parameters
📍 Path: Revenue and expense deferrals > Setup > Revenue and expense deferral parameters
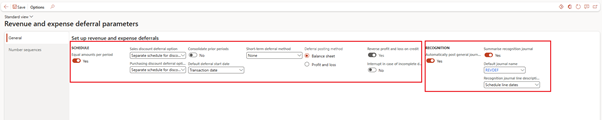
🧠 What It Does:
Sets global behaviour for how deferral schedules behave across all modules.
✅ Tip: Enable batch processing to recognize revenue on a monthly cadence automatically.
| Field | Purpose | Recommended Use | Simple Use Case Example |
| Schedule | Default deferral schedule type – typically fixed | Leave as default; system generates based on templates | When you invoice £6,000 for SBX-RNW-ANN1, the schedule splits into 12 months automatically |
| Equal amount per period | Ensures each recognition period receives the same amount (straight-line) | ✅ Enable for subscription billing to enforce equal monthly recognition | Monthly £500 revenue from annual CRM billing even if Feb has fewer days |
| Sales discount deferral option | Controls whether sales discounts are deferred separately or merged with revenue | 🔄 Merge with revenue for simplicity unless discount tracking is audited separately | You give a 10% discount on onboarding → merged with revenue and deferred together |
| Purchasing discount deferral option | Same as above but for vendor-side deferrals (expense side) | 🔄 Merge for services like prepaid cloud hosting or consultant retainers | Deferring consultant invoices with volume discount bundled into total service |
| Consolidate prior periods | Allows catch-up postings for missed periods (e.g., late recognition starts) | ✅ Enable to prevent posting gaps if recognition is triggered late | If recognition starts in May for a contract beginning in April, April revenue will post together with May |
| Default deferral start date | Controls recognition start point after invoice | 🎯 Recommended: “Transaction date” for accuracy; consider “Rule of 15” if you want more predictable rules | Contract starting 10-April posts full April recognition if using “Rule of 15”; otherwise proration kicks in |
| Short-term deferral method | How system separates short-term vs long-term deferral balances for reporting | 📊 Use “Rolling period” to classify what’s earned in <12 months vs >12 months | Deferring £2,400 over 24 months splits £1,200 as short-term, £1,200 as long-term |
| Deferral posting method | Controls whether recognition posts to balance sheet or P&L directly | ✅ Use “Balance Sheet” to reflect Deferred Revenue correctly | Deferred revenue goes to liability account (e.g., 222100) then recognized into P&L (e.g., 401100) |
| Reverse profit and loss on credit | Reverses P&L recognition if credit note is applied | ✅ Enable to cleanly reverse recognized revenue when issuing credit | Customer cancels 3 months into annual contract → 3 months already recognized are reversed |
| Interrupt in case of incomplete deferral entry | Prevents schedule generation if key config is missing | ✅ Enable for better data control – avoids partial/incomplete postings | If a product doesn’t have a template linked, the invoice won’t create a faulty deferral |
🧾 Recognition Tab
| Field | Purpose | Recommended Use | Simple Use Case Example |
| Automatically post general journals | Enables automatic posting of revenue recognition journals via batch | ✅ Enable to reduce manual month-end work | Each month, £500 of SBX-RNW-ANN1 revenue is recognized automatically |
| Summarise recognition journal | Combines multiple lines into one summary line per period | ✅ Enable unless detailed line posting is required for audit | All CRM subscriptions for April show 1 journal line: “Deferred → Revenue = £50,000” |
| Default journal name | Sets the journal name used for posting recognition | Use a dedicated journal like REVDEF for clarity | Keeps deferral entries separate from AP/AR and operational journals |
| Recognition journal line description | Controls what appears in the journal description | 🎯 Use “Schedule line dates” for clear period indicators | Journal line description = “Apr 2025 – SBX-RNW-ANN1” makes reconciliation easier |
⚙️ 2. Default Templates
📍 Path: Revenue and expense deferrals > Setup > Default templates
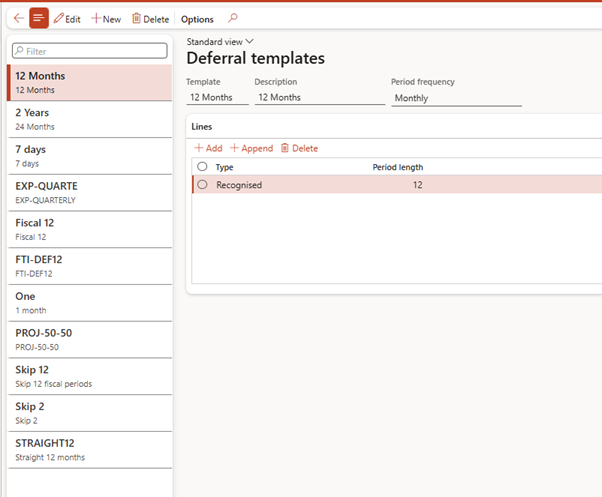
🧠 What It Does:
Assigns a default deferral template by transaction type—so users don’t have to select one manually each time.
| Default Template Use Case | Example Template |
| Sales order line deferral | STRAIGHT12 |
| Free text invoice deferral | FTI-DEF12 |
| Purchase order line deferral (for expense) | EXP-QUARTERLY |
| Project item deferral | PROJ-50-50 |
💡 You can override these at the line level when needed.
⚙️ 3. Deferral Defaults
📍 Path: Revenue and expense deferrals > Setup > Deferral defaults
🧠 What It Does:
Creates rules for assigning templates automatically based on conditions such as:
- Item group
- Account number
- Line property
- Category
🔍 Use Case:
Automatically assign a 12-month template to all CRM-related SKUs (SBX-RNW-ANN1) based on their item group.
| Field | Example Value |
| Account type | Customer |
| Account code | Group |
| Main account | 401100 (CRM Rev) |
| Item group | CRM-SUBS |
| Template | STRAIGHT12 |
🧠 Reduces setup error and ensures consistency across departments.
Purpose of Tabs
| Tab Name | Purpose | Effect on Deferral Process | Example (CRM SaaS Scenario) |
| Sales orders | Assigns deferral template, deferred revenue, deferred discount, consumption, and charge template for SO lines | Auto-generates schedule for each sales line item when invoiced | Auto-apply STRAIGHT12 to SBX-RNW-ANN1, including onboarding charge deferral |
| Purchasing | Assigns templates for deferring expenses and discounts on PO lines | Applies deferral when prepaying vendor retainers or long-term licenses | Defer consultant cost for onboarding support charged quarterly |
| General journal | Template for GL manual entries with deferrable revenue or cost | Supports ad hoc journal entries to defer prepaid revenue or costs | Manually post £24,000 revenue deferred over 24 months |
| Free text invoice | Assigns default deferral template for AR free text invoices | Automatically splits revenue when invoicing services outside sales orders | Use for invoicing a £1,200 CRM setup fee with 3-month straight-line recognition |
| Invoice journal | Template for posted invoice journals (manual or imported) | Ensures imported or external invoices are recognized over time | Imported legacy CRM renewals deferred using same STRAIGHT12 |
| Project fee | Assign deferred revenue and template for project-related fees | Aligns revenue recognition with project billing on fee-based services | Project onboarding fee deferred over 6 months |
| Project hours | Sets deferral rules for revenue and cost on time-tracked labor | Used to defer revenue (or cost) for hourly consulting tracked on project timesheets | Recognize 50% of consulting time after UAT completion |
| Project expense | Defers cost/revenue of recorded project expenses (travel, tools) | Useful when cost is incurred upfront, but delivery/value spreads over time | Defer internal training resource cost over project duration |
| Item requirement | Template for project item consumption (hardware or licenses issued to project) | Defer value recognition when item is consumed across milestones | Lease a phone for a 6-month project—cost/revenue recognized monthly |
| Expense template | Applies to recurring expense templates for employees | Useful for subscription-based employee tools or software | Defer cost of CRM license used by sales staff paid via employee expense reports |
| Timesheet | Assign templates to labor tracked via timesheets | Auto-recognizes cost and/or revenue based on tracked hours and period | Split onboarding consultant’s time across billing months |
⚙️ 4. Item Deferred by Default
📍 Path: Revenue and expense deferrals > Setup > Item deferred by default
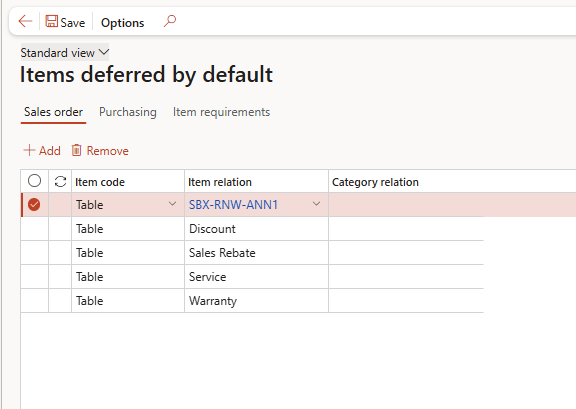
🧠 What It Does:
Allows you to mark specific items as deferrable without editing every product.
| Item Number | Description | Deferrable |
| SBX-RNW-ANN1 | Annual CRM Renewal | ✅ Yes |
| SBX-IMP-ONE | One-time Setup Fee | ❌ No |
💡 This flag ensures deferral is triggered automatically when this item appears on a document.
⚙️ 5. Deferrable Charges
📍 Path: Revenue and expense deferrals > Setup > Deferrable charges
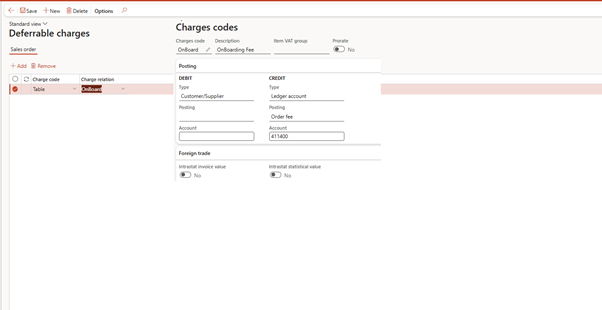
🧠 What It Does:
Identifies line-level charges (e.g., shipping, setup fees, adjustments) that should be included in the deferral.
| Charge Code | Description | Deferrable |
| SHIP-FEE | Shipping Fee | ❌ No |
| Handling | Onboarding Fee | ✅ Yes |
⚠️ Charges marked as deferrable will be split and recognized over time with the related revenue line.
⚙️ 6. Event-Based Deferrable Defaults
📍 Path: Revenue and expense deferrals > Setup > Event-based deferrable defaults
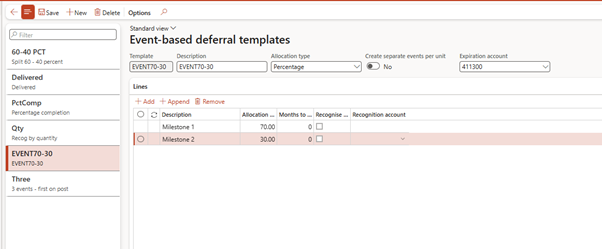
🧠 What It Does:
Allows you to configure deferral based on events, such as:
- Milestone completed
- Project task finished
- Manual confirmation
| Event Type | Default Template |
| Milestone 1 | EVENT70-30 |
| Milestone 2 | EVENT30 |
🔁 Used heavily for project-based, milestone-driven billing like SBX-MILET-01.
⚙️ 7. Assign Revenue Recognition Document to Imported Deferral Schedule
📍 Path: Revenue and expense deferrals > Setup > Assign rev. rec. doc. to imported deferral schedule
🧠 What It Does:
When importing deferral schedules (e.g., from legacy systems or external data), this tool allows you to link them back to source documents like:
- Sales orders
- Projects
- Invoices
📎 Ensures traceability of historical deferrals or externally-generated contracts.
✅ Summary
This article covered all setup entities in the Revenue and Expense Deferrals module—each playing a vital role in automating recognition logic.
| Setup Area | Use Case | Outcome |
| Revenue & Expense Deferral Parameters | Global journal posting & recognition logic | Controls how recognition behaves |
| Default Templates | Auto-assign templates by document type | Saves time and avoids manual errors |
| Deferral Defaults | Assign based on conditions like item group | Consistent, rule-based template selection |
| Item Deferred by Default | Tag specific products for deferral | Enables deferral without per-line toggle |
| Deferrable Charges | Include/exclude extra charges from deferral | Ensures total billing is accurately recognized |
| Event-Based Defaults | Trigger deferrals when milestones are completed | Supports project and onboarding scenarios |
| Import Linkage (Rev Doc Mapping) | Connect imported schedules to source docs | Maintains audit trail and historical linkage |
🔜 Coming Up Next: SB515 – Deferral Schedule Generation and Journal Entry Posting
In SB515, we’ll look at how deferral schedules are generated once an invoice posts, how revenue is recognized monthly via journal entries, and how to monitor the entire process.
We’ll show both:
- Automatic posting via batch
- Manual recognition for milestone events
- Journal previews and GL impact with real examples
Expand Your Knowledge: See More Subscription Billing Blogs
I am Yogeshkumar Patel, a Microsoft Certified Solution Architect and Enterprise Systems Manager with deep expertise across Dynamics 365 Finance & Supply Chain, Power Platform, Azure, and AI engineering. With over six years of experience, I have led enterprise-scale ERP implementations, AI-driven and agent-enabled automation initiatives, and secure cloud transformations that optimise business operations and decision-making. Holding a Master’s degree from the University of Bedfordshire, I specialise in integrating AI and agentic systems into core business processes streamlining supply chains, automating complex workflows, and enhancing insight-driven decisions through Power BI, orchestration frameworks, and governed AI architectures. Passionate about practical innovation and knowledge sharing, I created AIpowered365 to help businesses and professionals move beyond experimentation and adopt real-world, enterprise-ready AI and agent-driven solutions as part of their digital transformation journey. 📩 Let’s Connect: LinkedIn | Email 🚀
















Post Comment